
4.2 Structure of Atoms SPM Science
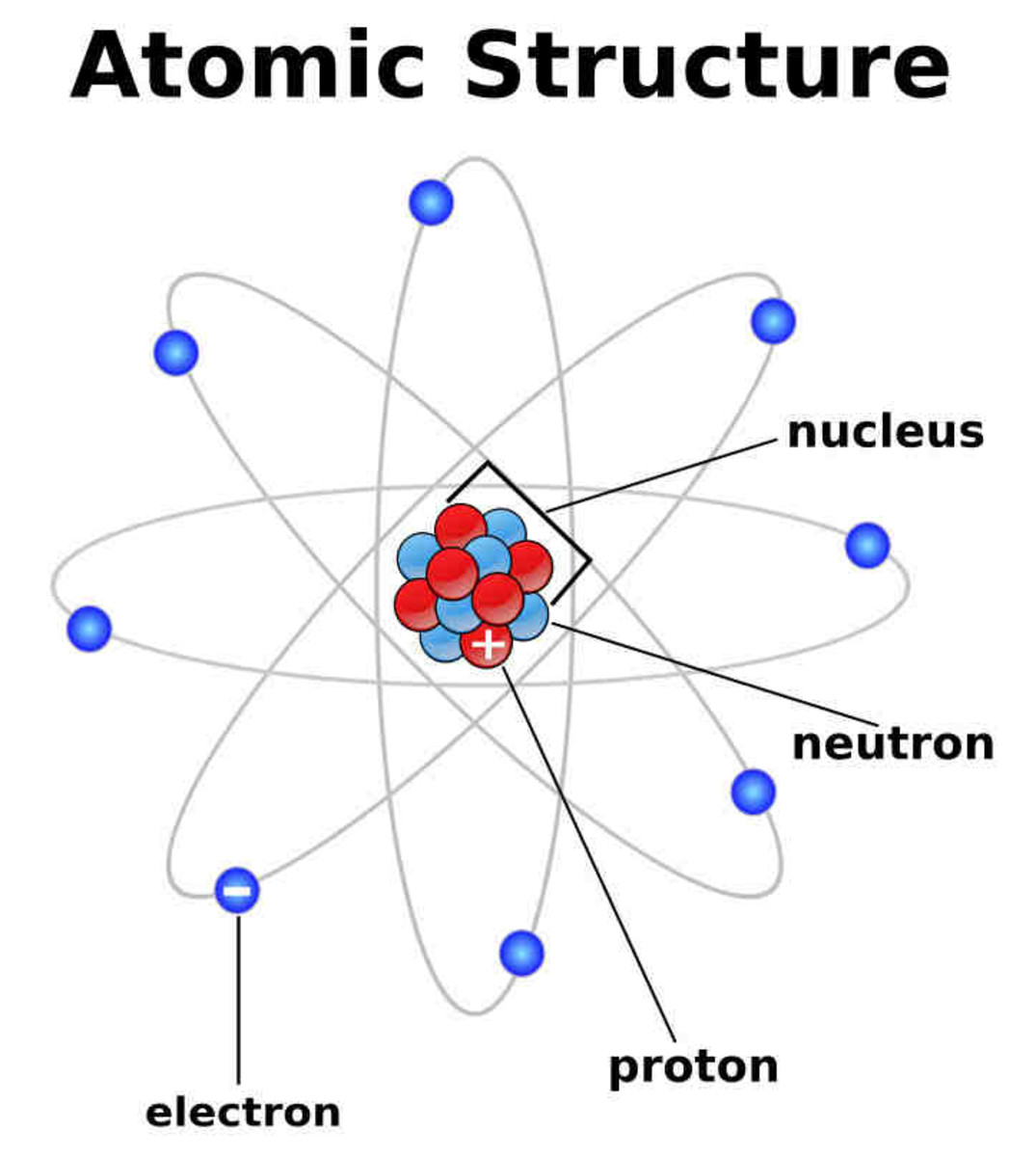
The atomic structure of these building blocks is very interesting. The protons and neutrons are located in the center of the atom, while the electrons are quite far from the center. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom determines its atomic number and its identity as a specific element. For example, all hydrogen atoms have one proton.
Atoms and Atomic Structure HubPages
Atom The atom is the basic particle of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically-bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished from each other by the number of protons that are in their atoms.

The Structure of the Atom GCSE Physics Science) AQA
The following diagram summarizes the basic facts of the structure of the atom. ATOM NUCLEUS The nucleus is the center of mass (A), but does not significantly contribute to volume. It is made up of: PROTONS: Mass = 1 amu, charge = +1 NEUTRONS: Mass = 1 amu, charge = 0 ELECTRONS

Atomic Structure & The Changing Models of Atom
nucleus . This is surrounded by electrons arranged in shells. The nucleus is tiny compared to the atom as a whole: the radius of an atom is about 0.1 nm (1 × 10 -10 m) the radius of a nucleus (1 ×.

ATOM, ORBITS AND ENERGY LEVELS » PIJA Education
Atoms are the foundation of chemistry. They are the basis for everything in the Universe. As you know, matter is composed of atoms. Solids are made of densely packed atoms while gases have atoms that are spread out. We're going to cover basics like atomic structure and bonding between atoms. As you learn more, you can move to the reactions and.
Atomic structure of matter, Energy levels, Electronic distribution
The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +12 m s = + 1 2 ).
/GettyImages-141483984-56a133b65f9b58b7d0bcfdb1.jpg)
Basic Model of the Atom Atomic Theory
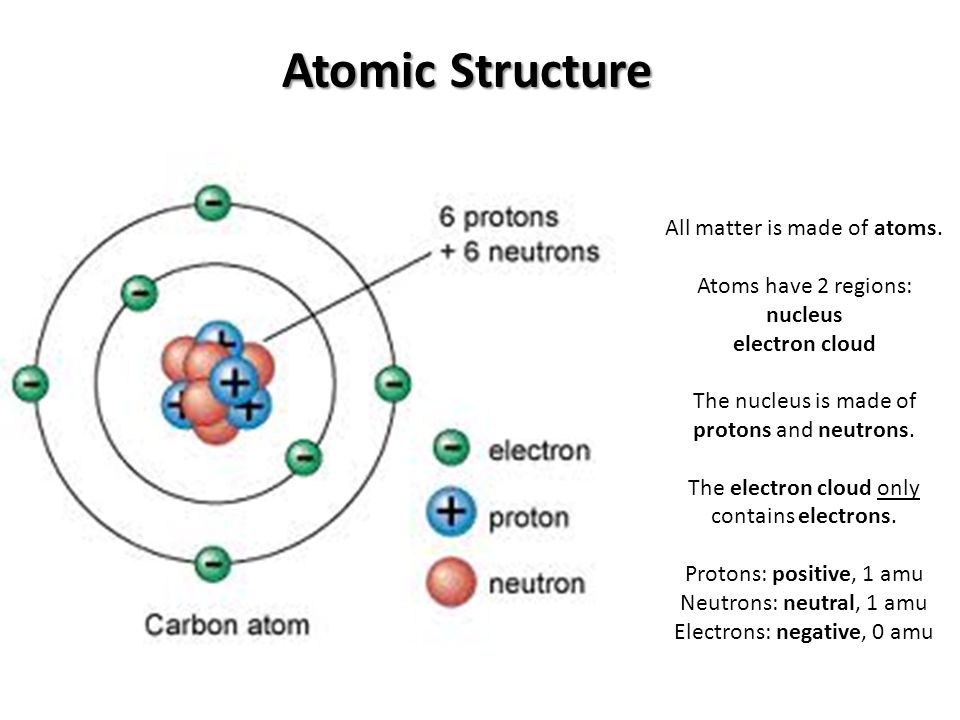
Figure 2.2.1 2.2. 1: The Structure of the Atom. Atoms have protons and neutrons in the center, making the nucleus, while the electrons orbit the nucleus. The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different.

Atomic Structure Broad Learnings
Physical Chemistry (Essentials) - Class 11 8 units · 52 skills. Unit 1 Welcome to physical chemistry. Unit 2 Structure of atom. Unit 3 Some basic Concepts of Chemistry. Unit 4 Redox reactions. Unit 5 Gaseous state. Unit 6 Thermodynamics. Unit 7 Chemical Equilibrium. Unit 8 Ionic equilibrium.

Structure Of An Atom Class 9 Science Notes Leverage Edu
Map: Chemistry - The Central Science (Brown et al.) 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
Lets Get Inside An Atom!! The Science Station
Most of the mass of an atom is in the nucleus, while the orbiting electrons account for an atom's size. As a result, an atom consists largely of empty space. Rutherford called his description the "planetary model" of the atom. Figure 2.3.2 2.3. 2 shows how this model explains the experimental results.
What is an Atom? Definitions & Examples Let us learn Basics News Bugz
Atom. Atoms are tiny particles that form the basic building blocks of all matter in the universe, whether solid, liquid, or gas. All living organisms and nonliving objects found on Earth are made of trillions and trillions of atoms. The smaller particles that make up an atom are known as subatomic particles. The term 'atom' was derived from.

Learn the Parts of an Atom
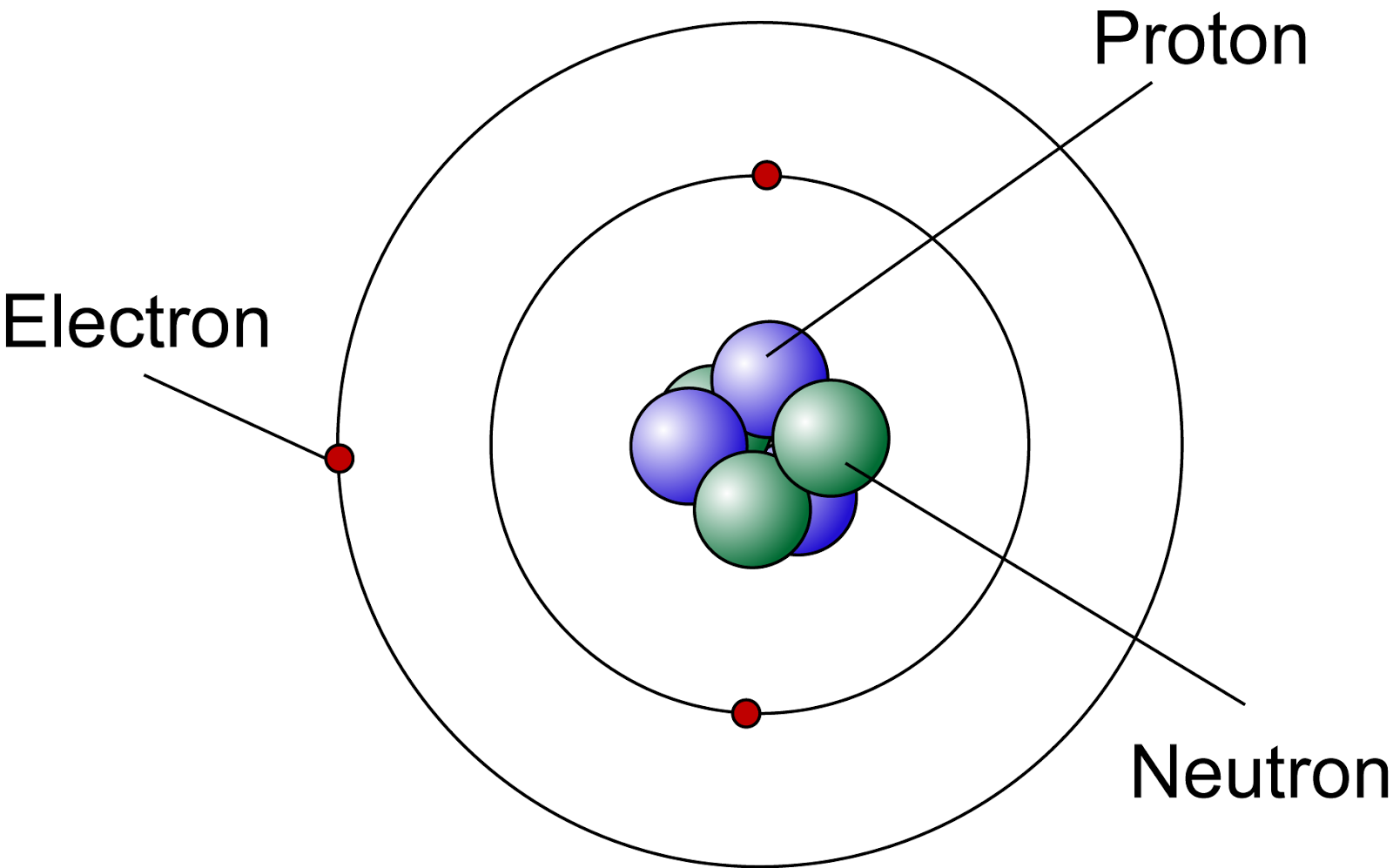
Atomic structure is the structure of an atom that consists of a nucleus (the centre), protons (positively charged), and neutrons (neutral). The electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus's centre. Democritus came up with the concept that matter is composed of atoms.
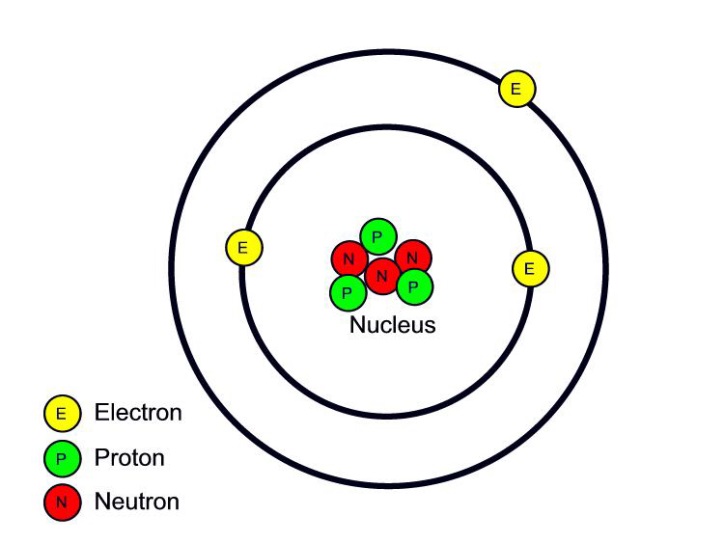
Atomic structure WGHS Junior Science
Basic Diagram of an Atom Most of an atom is just empty space and consists of a positively charged nucleus of protons and neutrons surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The center of an atom is the nucleus and one or more electrons surrounding the nucleus.
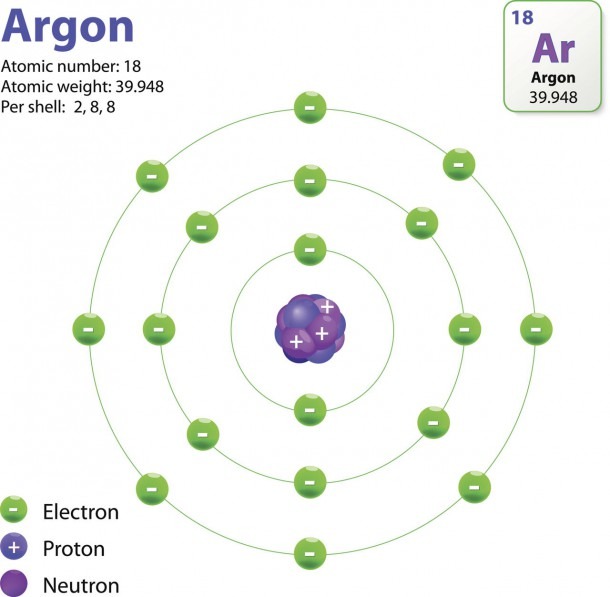
The Structure Of An Atom Explained With A Labeled Diagram Best
By convention, elements are organized in the periodic table, a structure that captures important patterns in their behavior.Devised by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) in 1869, the table places elements into columns—groups—and rows—periods—that share certain properties.These properties determine an element's physical state at room temperature—gas, solid, or liquid.
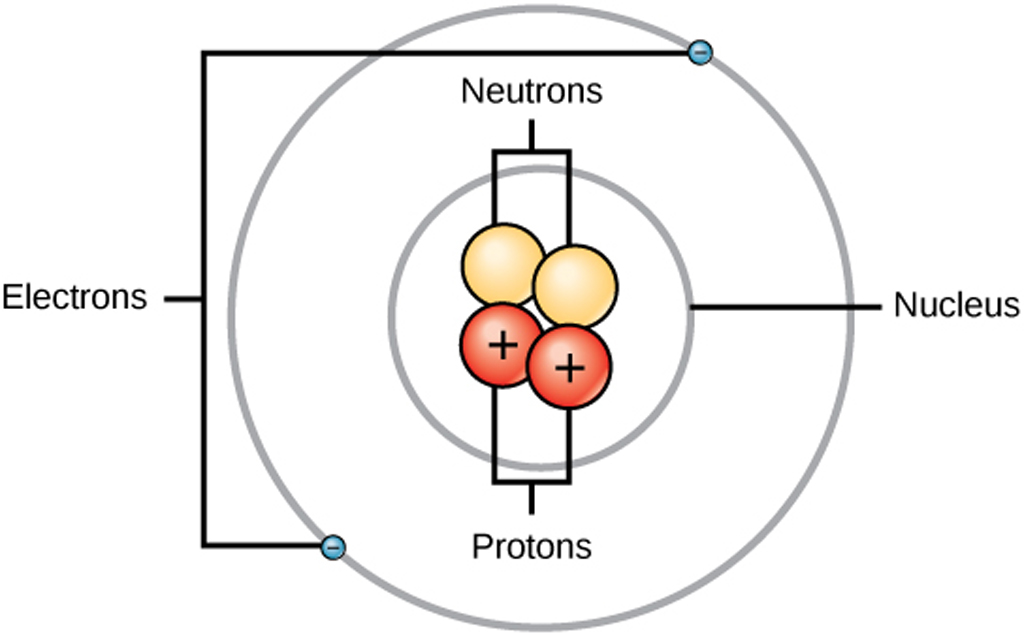
Structure of an Atom Structure & Use of Electron & Proton in Electronics
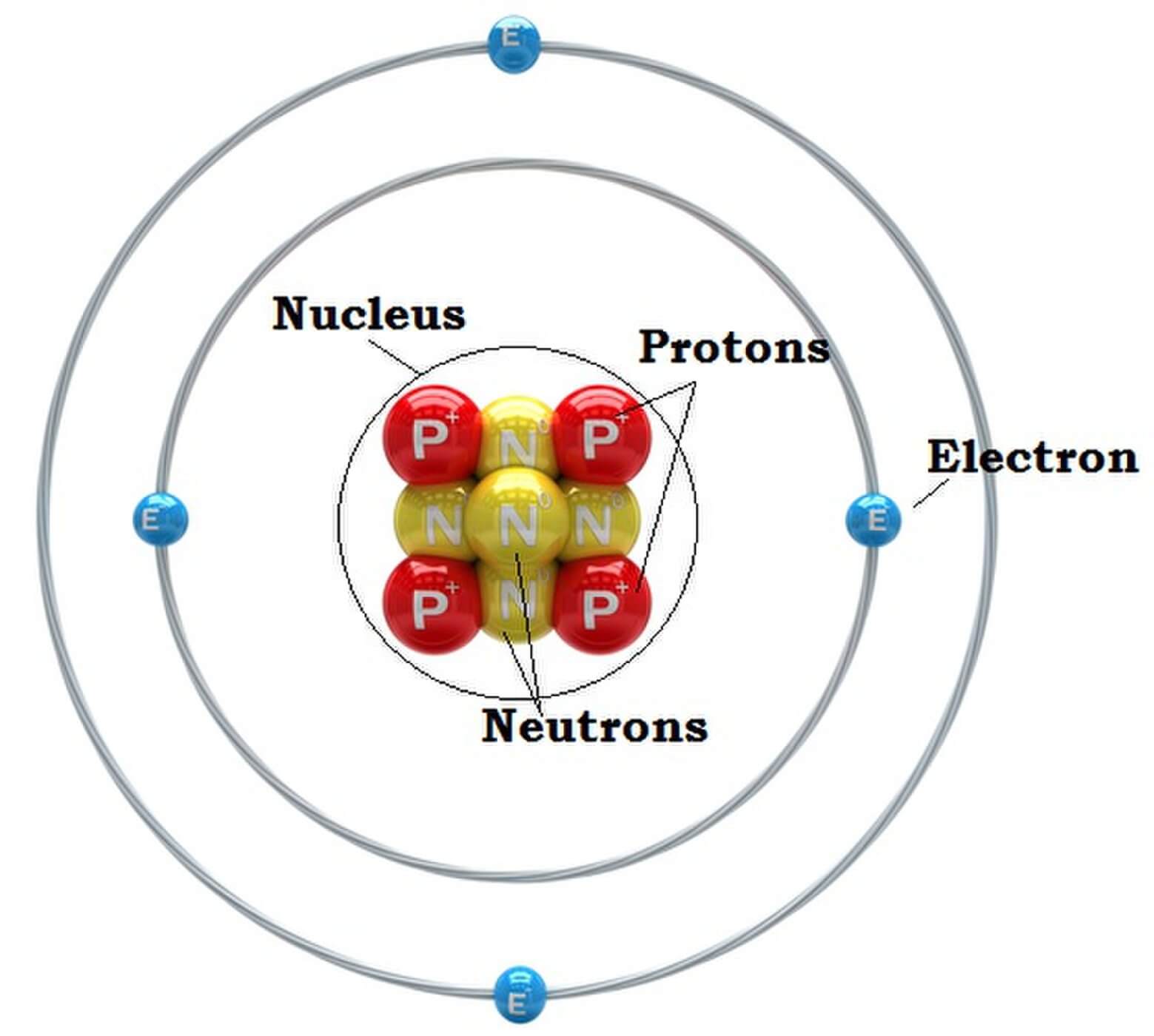
The atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. Download Complete Chapter Notes of Structure of Atom Download Now

Chemical bonding Atomic structure and bonding Britannica
Draw your protons and neutrons. Erase the "C" in the center circle, and draw in your protons. Since protons are the same as the amount of electrons, you just draw 6 protons. To indicate they are protons, draw them as circles with plus signs contained inside. Neutrons are simply equal to the atomic mass minus the number of protons.